把去年学到的东西,没说过的拼接一下,回见了您。 (之前名称叫 Hadoop 额外技能,不能就这样就和老博客同步,索性把大作业里面我顺手提到的东西都罗列一通)
C++ 大作业技术罗列
C++ 大作业学到的偏门东西。
va_list 对象
不用 printf() 函数,运用 cstdarg 库实现类似该函数的 error()。
- 函数原型
void error(const char *format, ...)
- 算法
- 生成
va_list对象,然后初始化。 - 通过对母字符串的逐个字符读取,判断以下情况:
- 如果不是
%直接输出。 - 如果是
%, 后面跟着是:输入 | 输出 | s | 字符串 | c | 字符 | d | 整型数 | % | %符号 |
- 如果不是
- 注意判断字符还是整数的时候,先按照整型数读入,然后按情况强制类型转换看看。
cstdarg函数库怎么搞不定长形参的?
- 形参的最后一定要是省略号。
va_list规定一个不定长形参变量。va_start让其找到开始位置,之后va_arg向后读取一个参数。va_end终止va_list存在。
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdarg>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void error(const char *format, ...)
{
va_list ap;
va_start(ap, format);
string toOutput = format;
for (int i = 0; i < toOutput.size(); ++i)
{
if (toOutput[i] == '%')
{
i++;
if (toOutput[i] == '%')
{
cout << '%';
}
else if (toOutput[i] == 's')
{
string a = va_arg(ap, const char *);
cout << a;
}
else
{
int a = va_arg(ap, int);
if (toOutput[i] == 'c')
{
cout << (char)a;
}
else if (toOutput[i] == 'd')
{
cout << a;
}
}
}
else
{
cout << toOutput[i];
}
}
va_end(ap);
}
int main()
{
error("Hello %s, %d, %c. %%\n", "SuperBart", 'f', 'f');
// For test.
printf("Hello %s, %d, %c. %%\n", "SuperBart", 'f', 'f');
}
如何更加省心地随便编个数
- 先引入 C++ 11 标准的全新标准库
random。 - 先找个能生成随机种子的随机数引擎,我用的是
random_device,在 Linux 上相当于读取/dev/urandom产生的随机数。我们不使用该引擎生成随机数,因为根据原理,在生成随机数的时候,会产生大量的输入输出中断,一定程度上影响性能,而且会下降/dev/urandom生成随机数的质量。 - 然后利用上述引擎,生成我们要用的引擎
default_random_engine。 - 我们利用该随机数引擎,生成随机数。由于我们这里使用无符号的随机数,遵循均匀分布,我们使用
uniform_int_distribution<uint>类来生成之。 顺便说一句,random库还能支持你在概率论课程上学到的所有玩意,比如万恶的正态分布,泊松分布啥的。
如何在虚拟机之间搞互联互通?—— 以 VirtualBox 为示例
为了 Hadoop 的主从模式,我搞了三个虚拟机。
概述
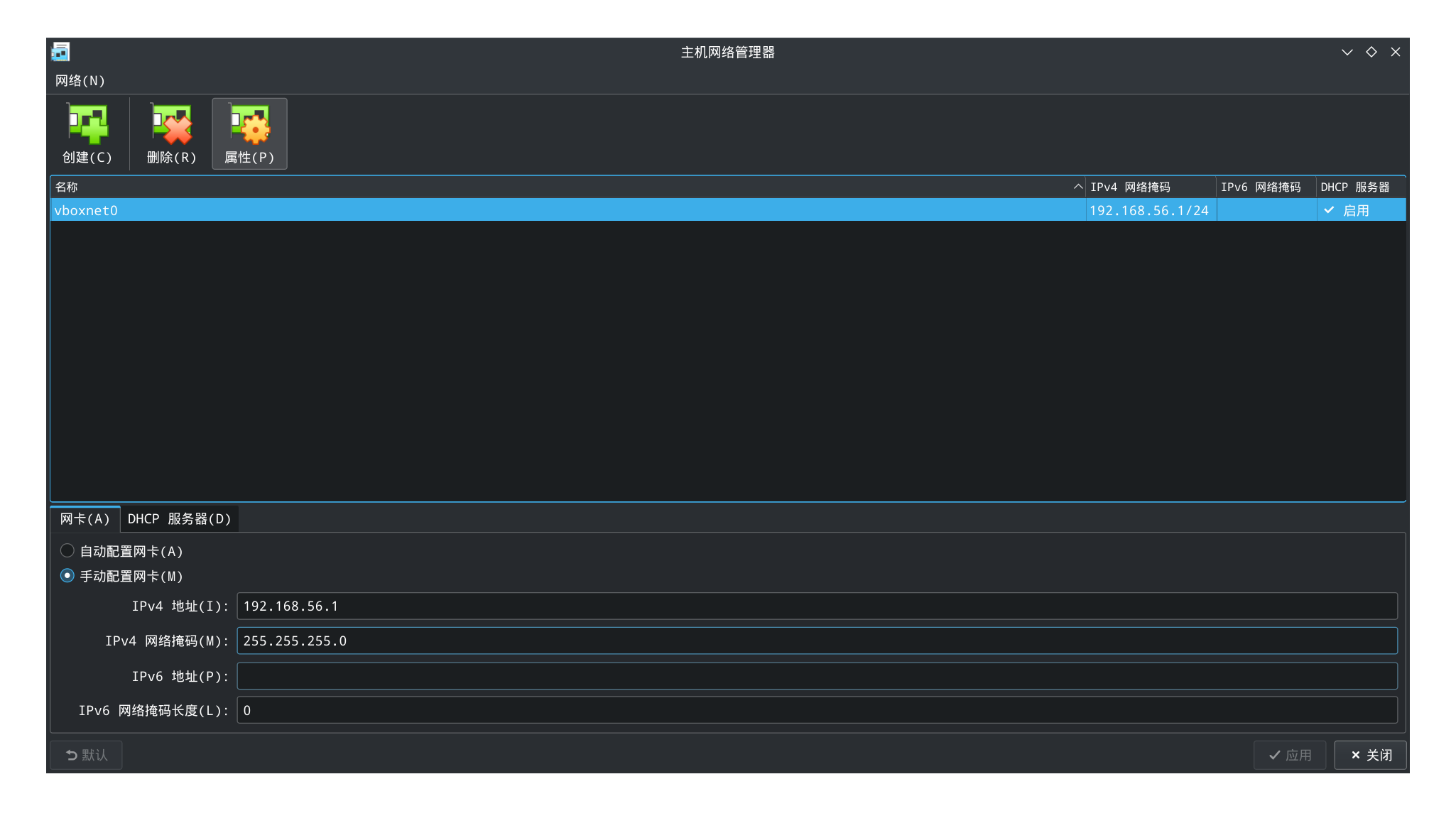
- 管理 -> 主机网络管理器新建一个新网卡 vboxnet0
- 在每个虚拟机的设置中,设置网络为仅主机网络,界面名称 vboxnet0
- 每个虚拟机里面要设置好固定 ip ,关闭防火墙,和 ssh 免密码登录
- (可选但推荐) 修改所有虚拟机的 host 文件,标记所有虚拟机的地址
截图~主机网络管理器
如果设置成功的话,你的宿主机应该可以 ping 到你的虚拟机。查看你电脑的 ip,可以执行 ifconfig 或者 ip a。
如何关闭网络防火墙
基本上我见到的 Linux 系统,防火墙软件都是 firewalld。关闭防火墙,也就是关掉这个服务。所以我们要执行
sudo systemctl stop firewalld.service # 停止防火墙服务
sudo systemctl disable firewalld.service # 防止防火墙开机自启动
说到这了,看看 Systemd 还能搞啥
sudo systemctl status firewalld.service # 看看这玩意运行状态
另外,如果你安装的是 Ubuntu Server ,安装时候可以关掉防火墙选项的。如果你安装的是 OpenSUSE,你也可以在 YaST 里面关掉,或者开 22 和 23 端口。
如何设置免密码登录 ssh
$ ssh-keygen
$ cd ~/.ssh
$ ssh-copy-id 另外一个虚拟机的用户名@另外一个虚拟机的ip
$ ssh 另外一个虚拟机的用户名@另外一个虚拟机的ip # 测试是否成功
注意,.ssh目录的权限为700,其下文件authorized_keys和私钥的权限为600。如有问题,请使用 chmod 修改。
修改 Host 文件
sudo nano /etc/hosts
修改方式是 ip + 电脑名称
C 语言的 SQLite 函数概览
为啥是 C 语言的,因为 Vala 的 SQLite 支持是把 C 语言支持的头文件给“照搬”了。
基础函数
通过这个方式来创建一个 SQLite 结构体:
sqlite *db;
通过这个方式,打开一个数据库:
int sqlite3_open(
const char *filename, /* 文件所在的路径 */
sqlite3 **ppDb /* 对应的 SQLite 结构体 */
);
通过这个方式,来在这个数据库上执行 SQL 语句:
int sqlite3_exec(
sqlite3*, /* 要执行的数据库 */
const char *sql, /* 执行语句 */
sqlite_callback, /* 回调 */
void *data, /* 回调参数 */
char **errmsg /* 接受错误信息的字符串 */
);
使用完数据库后,通过这个函数释放数据库。
int sqlite3_close( sqlite3* /* 你需要关闭的数据库 */ );
函数返回值
SQLite 里面的函数在执行的时候,都会有一个返回值。在 C 语言头文件里面,是一堆 define 。以下是 sqlite3.h 文件里面的东西。
/*
** sqlite3.h, version 3.40.0, line 433-476.
**
** CAPI3REF: Result Codes
** KEYWORDS: {result code definitions}
** 返回值 要点:返回值和定义
**
** Many SQLite functions return an integer result code from the set shown
** here in order to indicate success or failure.
** 许多 SQLite 函数的返回值是下面定义的整型,以反映成功/失败状态。
**
** New error codes may be added in future versions of SQLite.
** 新的错误码将会在未来版本加入。
**
** See also: [extended result code definitions]
** 还有扩充版返回值定义:-P
*/
#define SQLITE_OK 0 /* Successful result */
/* beginning-of-error-codes */
/* 除了0之外全是出错 */
#define SQLITE_ERROR 1 /* Generic error */
#define SQLITE_INTERNAL 2 /* Internal logic error in SQLite */
#define SQLITE_PERM 3 /* Access permission denied */
#define SQLITE_ABORT 4 /* Callback routine requested an abort */
#define SQLITE_BUSY 5 /* The database file is locked */
#define SQLITE_LOCKED 6 /* A table in the database is locked */
#define SQLITE_NOMEM 7 /* A malloc() failed */
#define SQLITE_READONLY 8 /* Attempt to write a readonly database */
#define SQLITE_INTERRUPT 9 /* Operation terminated by sqlite3_interrupt()*/
#define SQLITE_IOERR 10 /* Some kind of disk I/O error occurred */
#define SQLITE_CORRUPT 11 /* The database disk image is malformed */
#define SQLITE_NOTFOUND 12 /* Unknown opcode in sqlite3_file_control() */
#define SQLITE_FULL 13 /* Insertion failed because database is full */
#define SQLITE_CANTOPEN 14 /* Unable to open the database file */
#define SQLITE_PROTOCOL 15 /* Database lock protocol error */
#define SQLITE_EMPTY 16 /* Internal use only */
#define SQLITE_SCHEMA 17 /* The database schema changed */
#define SQLITE_TOOBIG 18 /* String or BLOB exceeds size limit */
#define SQLITE_CONSTRAINT 19 /* Abort due to constraint violation */
#define SQLITE_MISMATCH 20 /* Data type mismatch */
#define SQLITE_MISUSE 21 /* Library used incorrectly */
#define SQLITE_NOLFS 22 /* Uses OS features not supported on host */
#define SQLITE_AUTH 23 /* Authorization denied */
#define SQLITE_FORMAT 24 /* Not used */
#define SQLITE_RANGE 25 /* 2nd parameter to sqlite3_bind out of range */
#define SQLITE_NOTADB 26 /* File opened that is not a database file */
#define SQLITE_NOTICE 27 /* Notifications from sqlite3_log() */
#define SQLITE_WARNING 28 /* Warnings from sqlite3_log() */
#define SQLITE_ROW 100 /* sqlite3_step() has another row ready */
#define SQLITE_DONE 101 /* sqlite3_step() has finished executing */
/* end-of-error-codes */
看看 SQLite 的头文件吧,很详细的。
使用 SQLite 声明
使用 SQLite 声明来执行 SQL 语句,比直接调用 exec 更高效。
首先,你需要写好一个 SQL 语句,碰到待定的地方可以用问号,或者 $xxx 等形式表示。以下是我程序里面的示例:
private const string ADD_HOTEL_DATA = """
INSERT INTO HOTEL (location, price, numRooms, numAvail)
VALUES ($LOCATION, $PRICE, $NUMBEROFROOMS, $NUMBEROFAVALIABLE);
""";
然后使用这个函数,准备声明:
sqlite3_stmt *stmt = NULL; /* 先初始化一个空的 */
int sqlite3_prepare_v2(
sqlite3 *db, /* 需要用到的数据库 */
const char *zSql, /* SQL 语句 */
int nByte, /* 字符串长度 */
sqlite3_stmt **ppStmt, /* OUT: 指向一个需要初始化的声明 */
const char **pzTail /* OUT: 貌似是说 SQL 声明的尾部,可以不管吧 */
);
然后,使用 sqlite_bind系列函数在声明上绑定变量,以下用 sqlite3_bind_text 举例:
int sqlite3_bind_text(
sqlite3_stmt*, /* 需要用到的声明 */
int, /* 在声明需要绑定位置的索引,从 1 开始计数 */
const char*, /* 需要绑定的字符串 */
int, /* 字符串的长度 */
void(*)(void*) /* 某种析构函数,当绑定失败执行这个吧 */
);
还有 sqlite3_bind_int,sqlite3_bind_double之类,用法都差不多。
注意,你可以用这个函数寻找声明里面的索引:
int sqlite3_bind_parameter_index(
sqlite3_stmt*, /* 需要用到的声明 */
const char *zName /* 需要寻找的绑定位置 */
);
如果没找到的话,就返回 0。
现在你可以执行绑定完变量的声明了。
int sqlite3_step( sqlite3_stmt* /* 需要用到的声明 */ );
这个函数执行完,有三个状态:SQLITE_DONE,SQLITE_ROW和各种报错。接下来我们关注 ``SQLITE_ROW`,也就是返回一条行记录的状况,这个一般会出现在执行了 SELECT 的情况。
我们使用 sqlite_column系列函数取出这些东西,先输入使用到的声明,然后输入索引,返回值就是里面的数据。
const void *sqlite3_column_blob(sqlite3_stmt*, int iCol);
double sqlite3_column_double(sqlite3_stmt*, int iCol);
int sqlite3_column_int(sqlite3_stmt*, int iCol);
sqlite3_int64 sqlite3_column_int64(sqlite3_stmt*, int iCol);
const unsigned char *sqlite3_column_text(sqlite3_stmt*, int iCol);
const void *sqlite3_column_text16(sqlite3_stmt*, int iCol);
sqlite3_value *sqlite3_column_value(sqlite3_stmt*, int iCol);
int sqlite3_column_bytes(sqlite3_stmt*, int iCol);
int sqlite3_column_bytes16(sqlite3_stmt*, int iCol);
int sqlite3_column_type(sqlite3_stmt*, int iCol);
清除绑定,使用如下函数:
int sqlite3_reset(sqlite3_stmt *pStmt /* 需要用到的声明 */ );
删除声明,使用如下函数:
int sqlite3_finalize(sqlite3_stmt *pStmt /* 需要删除的声明 */ );
举个 CPP 里面的例子
目前我没有找到能让我舒心使用的 CPP SQLITE 库。
#include <cstddef>
#include <sqlite3.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
/*======================================
Data Structure
======================================*/
struct TeacherDS {
string Tno;
string Tname;
string Tele;
string TRS;
string Pass;
};
typedef map<int, vector<pair<int,int>>> TimeInformation;
/*======================================
Database Class
======================================*/
// Database class
struct Database {
private:
sqlite3 *db;
public:
int rc;
char *zErrMsg = 0;
private:
bool create();
public:
Database();
~Database();
void exec(string sql); // For insert and delete.
TimeInformation get_spare(); // Query the empty time in 2022-12-31.
};
// Create an new database file.
bool Database::create() {
// Create an empty database.
rc = sqlite3_open_v2("management.db", &db, SQLITE_OPEN_READWRITE | SQLITE_OPEN_CREATE, NULL);
if( rc ) {
cout << "Can't create database: " << rc << ", " << sqlite3_errmsg(db) << endl;
return false;
}
// Create new table.
const char *create_table_queries =
"CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Teacher ( Tno VARCHAR(10), Tname VARCHAR(20), Tele VARCHAR(20) , TRS VARCHAR(30) ,Pass VARCHAR(40),PRIMARY KEY (Tno));"
"CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Instrument ( Ino VARCHAR(10), Iname VARCHAR(20), Stat VARCHAR(10),PRIMARY KEY (Ino));"
"CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Manage( Ino VARCHAR(10),Lno VARCHAR(10),PRIMARY KEY (Ino,Lno),FOREIGN KEY (Ino)REFERENCES Instrument(Ino),FOREIGN KEY (Lno)REFERENCES Lab(Lno) );"
"CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Lab( Lno VARCHAR(10), Lname VARCHAR(40), People INT ,Purpose VARCHAR(40),Time INT,PRIMARY KEY (Lno));"
"CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Orders( Tno VARCHAR(10), Lno VARCHAR(10), Users VARCHAR(30) ,Btime DATETIME,Etime DATETIME,PRIMARY KEY (Tno,Lno,Btime,Etime),FOREIGN KEY (Tno)REFERENCES Teacher(Tno),FOREIGN KEY (Lno)REFERENCES Lab(Lno) );"
"CREATE VIEW IF NOT EXISTS SJ_PROJECT AS SELECT Sno,Pno,Qty FROM SPJ,J WHERE Jname = '三建' AND J.Jno = SPJ.Jno;";
rc = sqlite3_exec(db, create_table_queries, 0, 0, &zErrMsg);
if( rc ) {
cout << "Can't create tables: " << rc << ", " << sqlite3_errmsg(db) << endl;
return false;
}
cout << "Created database successfully" << endl;
return true;
}
Database::Database() {
rc = sqlite3_open_v2("management.db", &db, SQLITE_OPEN_READWRITE, NULL);
if( rc ) {
cout << "Can't open database: " << rc << ", " << sqlite3_errmsg(db) << endl;
if (!create()) {
return;
}
} else {
cout << "Opened database successfully." << endl;
}
}
Database::~Database() {
sqlite3_close_v2(db);
}
void Database::exec(string sql) {
rc = sqlite3_exec(db, sql.c_str(), 0, 0, NULL);
if( rc ) {
cout << "Can't execute this sql line: " << sql.substr(0,15) << "... with the following error: " << rc << ", " << sqlite3_errmsg(db) << endl;
}
}
TimeInformation Database::get_spare() {
TimeInformation toReturn, occupied;
string sql = "select * from Spare_Time";
sqlite3_stmt *stmt = NULL;
rc = sqlite3_prepare_v2(db, sql.c_str(), sql.length(), &stmt, NULL);
if( rc ) {
stringstream error;
error << "Can't prepare statement: " << rc << sqlite3_errmsg(db) << endl;
throw error.str();
}
while (sqlite3_step(stmt) == SQLITE_ROW) {
occupied[sqlite3_column_int(stmt,0)].push_back({
sqlite3_column_int(stmt,1),
sqlite3_column_int(stmt,2)
});
}
// Too crap to write, because my math is taught by Cirno:-P
for (auto i : occupied){
int start = 8;
int end = 9;
for (auto j : i.second) {
if (start != j.first) {
end = j.first;
toReturn[i.first].push_back({start,end});
}
start = j.second;
end = start + 1;
}
if (start <= 20) {
toReturn[i.first].push_back({start,20});
}
}
for (auto i : toReturn) {
cout << i.first << ": ";
for (auto j : i.second) {
cout << j.first << "-" << j.second << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << "Rest of the Lab are all avaliable from 8 to 20." << endl;
return toReturn;
}
// Entry formula.
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
cout << "Lab manage system initialing..." << endl;
Database db = Database();
if (db.rc != SQLITE_OK) {
return 1;
}
if (argc == 2 && strcmp(argv[1],"--query") == 0) {
cout << "Query the empty time in 2022-12-31." << endl;
db.get_spare();
} else {
cout << "Lab manage system instructions." << endl;
cout << "Usage: lab-management [option]" << endl;
cout << "Options: " << endl;
// cout << " --user Login this system as teacher." << endl;
cout << " --query Query the empty time in 2022-12-31." << endl;
}
return 0;
}
自行了解用途,我已经忘了。